

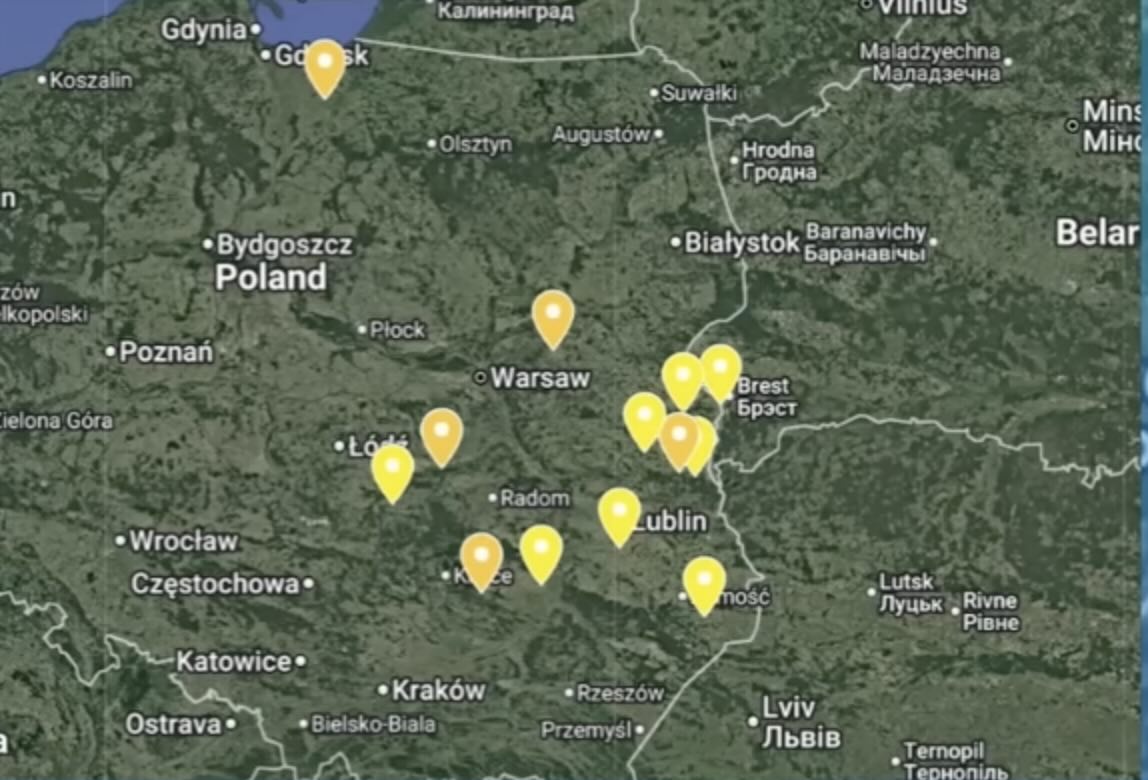
The pattern of debris south of Lublin and assessed routing towards Rzeszów–Jasionka—the principal trans-Atlantic logistics node for Ukraine—points to route design, software pre-programming and target rehearsal rather than opportunism.
The operational logic is straightforward. First, test the Alliance’s political and military reaction cycle to activity affecting a member state; measure detection, alerting and notification speeds; and observe the thresholds at which national and NATO assets are committed. Second, validate approach corridors for subsequent sorties by tracing areas of high radar density, exploiting coverage seams and skirting known air-defence positions. Rzeszów, receiving regular flights—including from the United States—before onward rail movement via Kraków–Rzeszów–Przemyśl to Lviv, is an obvious priority in any escalation scenario.
Early plots indicate launches from Belarusian territory on bearings towards Lublin, with a secondary mechanism in which drones initially heading for western Ukraine (notably the Lviv region) diverted into Polish airspace. This mixed routing complicates attribution and response authority in real time. Open-source mapping has clustered impact points slightly south of Lublin, pending official confirmation of each site. The tactical takeaway is that ingress routes are being iteratively refined to approach Polish assets while sampling sensor coverage across multiple sectors.
Markings photographed on at least one tail assembly—Cyrillic characters and numerals—are not dispositive. Defence-industrial serials often encode manufacturer, batch and date; equally, mislabelling to contaminate the forensic trail is routine tradecraft. Provenance rests on component analysis: airframe materials, guidance board signatures, powerplant type and GNSS dependencies.
Allied measures announced to date—French Rafales, additional RAF Typhoons and Dutch Patriot batteries for Poland—signal resolve, but they do not in themselves close the counter-UAS gap. High-end systems optimised for ballistic and cruise threats are a poor economic match against low-cost propeller drones. What matters at the border is a layered, mobile short-range defence: gun systems with airburst ammunition, MANPADS, rapid-cue electro-optical units, inexpensive radar and passive RF sensors, backed by electronic attack. The kill-chain problem is sensor-to-shooter latency and magazine depth, not platform prestige. Batteries that cannot afford to engage ten-to-one on cost will conserve missiles and accept leakage; Russia’s calculus relies on that arithmetic.
The Polish decision to dispatch a specialist team to Ukraine is practical. The Armed Forces of Ukraine have built a field-tested playbook for mass-raid defence: dispersed sensors feeding lightweight command posts; small mobile firing units that displace between waves; cross-cueing between radar, RF detectors and optical sights; and strict fire-discipline to husband interceptors for the highest-payoff shots. Transferring these methods—rather than simply importing hardware—addresses the real bottlenecks of training, procedures and emplacement.
The legal-political frame—Article 4 consultations versus Article 5 collective defence—remains sensitive to verified facts. Attribution, assessed intent and physical effects determine whether an incursion is treated as hostile reconnaissance, a coercive signal, or an attack. The present incidents fit the reconnaissance–rehearsal pattern: a stress test of Alliance cadence without overt escalation. That does not make them benign. Each rehearsal improves route knowledge and shortens the timeline to a strike on logistics nodes if Moscow elects to escalate.
For Poland and NATO, the analysis translates into concrete lines of effort:
Corridor denial. Identify and block the specific ingress routes sampled on 10 September by repositioning SHORAD and gun systems, deploying additional passive sensors, and using decoys to distort adversary learning.
Air policing versus wartime posture. Re-baseline alert states in the south-east to reflect a counter-UAS fight, not a peacetime QRA model built around fast-jet intercepts.
Civil–military integration. Tighten procedures around Rzeszów–Jasionka: NOTAM triggers, debris recovery, briefed diversion plans, and public information that does not compromise sensor siting.
Magazine and sustainment. Increase stocks of cheap effectors (airburst 30–35 mm, MANPADS, programmable fuzes) and standardise parts across units to keep mobile sections in the line.
Forensics at speed. Build a rapid technical exploitation chain for recovered fragments to close the loop on platform type, guidance mode and supplier networks, informing both targeting and sanctions policy.
The logistics picture deserves equal emphasis. The Kraków–Rzeszów–Przemyśl–Lviv axis concentrates rail junctions, fuel storage and transfer points. Even without confirmed physical damage in Poland from this episode, the flight paths are an intelligence marker of targeting intent. Hardening, redundancy and deception measures along that corridor should be treated as a priority, including dispersed off-loading sites, camouflage for high-value assets, and routine movement noise to mask genuine surges.
Three immediate analytical tasks follow. First, establish a verified timeline separating events over Poland and Ukraine, with precise launch windows and track plots. Secondly, assess Polish and allied sensor performance on the night—detection ranges against small radar cross-sections, false-alarm rates, and the hand-off from national systems to NATO air picture. Thirdly, test the alerting chain end-to-end, measuring minutes lost at each step from detection to engagement.
The 10 September incursions are best read as an instrumented rehearsal against a known logistics hub and its approaches. They exposed seams in coverage, highlighted the cost-exchange problem for high-end interceptors, and probed NATO’s reaction tempo. The corrective measures are equally well understood: more sensors, cheaper effectors, faster command chains, and mobility. The question is not conceptual but implementation at pace in the sector that Moscow is studying most intently.
If Russia Wins: A Scenario and the Logic of the West’s Managed Defeat